Key takeaways
-
Coding charts display open and close low (OHLC) data.
-
OHLC data helps traders track price movements, analyze volatility and identify trading opportunities.
-
The X axis represents time frames, while the Y axis displays price levels, either on a linear or logarithmic scale. Volume bars below the chart help confirm market participation.
-
Candlestick charts remain the most popular for their detail, while line charts provide quick overviews, and bar charts provide alternative analysis to OHLC.
-
Popular patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops and bottoms, triangles, flags, pennants and wedges capture a trader’s emotions and help predict potential reversals or continuations.
In 2025, cryptocurrencies remain a mixture of opportunities and challenges. Prices continue to fluctuate due to new regulations, new technology trends, and artificial intelligence that affect how the market moves.
For beginners, the market can feel overwhelming, but once you do… Learn how to read cryptographicsThe chaos begins to make sense.
This article explains how to read cryptocurrency charts by analyzing patterns and underlying tools and techniques. Whether you are trying to predict the price of Bitcoin (Bitcoin) Next step or next exploration Altcoin ralliesYou will gain practical skills to interpret price action. By taking a clear, step-by-step approach, it helps you build a solid foundation for cryptocurrency trading and avoid common mistakes.
Basics of encryption scheme
Cryptocurrency price charts visually represent price movements across different time frames, providing insight into trends, volatility, and price fluctuations. Trading opportunities. In the fast-paced cryptocurrency market, open and close low (OHLC) data allows investors to track price changes over specific periods, forming the core of technical analysis.
Main components
Understanding the structure of crypto charts is essential for traders. The main components of cryptographic schemes include:
-
X-axis: Multi-time frame analysis is key to balancing short-term trading with long-term forecasts. You can adjust charts from one minute to monthly intervals.
-
Y axis: The price scale can be set to linear or logarithmic. The logarithmic scale is more useful for long-term cryptocurrency analysis because it highlights percentage-based changes more clearly.
-
Size bars: These activities show market activity and help confirm chart patterns by indicating whether a breakout or reversal is supported by strong trading participation.
Types of foundation plans
Some types of charts form the basis of technical analysis. The most common include:
-
candlestick: The most commonly used chart type, which displays OHLC data within a single bar.
-
line: It provides a quick look at overall trends by correlating closing prices over time.
-
roadblock: An alternative to candlesticks that also displays the OHLC structure in a simpler format.
With the advent of artificial intelligence, graphs that integrate string data have emerged, e.g wallet Activity and Total Value Locked (TVL)has become increasingly popular. These advanced charts give traders deeper insights into evolving market dynamics.
Did you know? Candlestick charts originated in Japan in the 18th century, where they were first used to track rice trading, long before they arrived in modern cryptocurrency markets.
Five most common chart patterns in cryptocurrency trading
Chart patterns are shapes formed by price movements that help traders predict future market trends. These patterns fall into two main categories: reversal patterns, which indicate that the current trend may change direction, and continuation patterns, which indicate that the trend is likely to resume after a short pause. It stems from market psychology, where emotions such as fear, greed, and uncertainty drive mass trading behavior and create recognizable shapes on charts.
Here are five common patterns that every cryptocurrency investor, including beginners, should know:
1. Head and shoulders
The head and shoulders pattern features three peaks, with a higher intermediate peak (the head) between two smaller peaks (the shoulders), all connected by a “neckline.” A reversal indicates a potential bullish reversal.
-
How to read: Low volume on the right shoulder indicates weak momentum. A price break below the neckline confirms a bearish reversal, while a break above it confirms a bullish reversal. Measure the distance from the head to the neckline, then determine that distance from the breakout point to estimate the target movement.
-
Stop loss: Place it above the right shoulder for bearish settings or below it for bullish settings.
-
example: This pattern often appears during altcoin corrections after large hype cycles, such as following the listing of the token on a major exchange like Binance. In early 2025, Cardano (Ada) A head and shoulders pattern formed during the correction phase after the management upgrade hype, indicating a temporary downward movement.
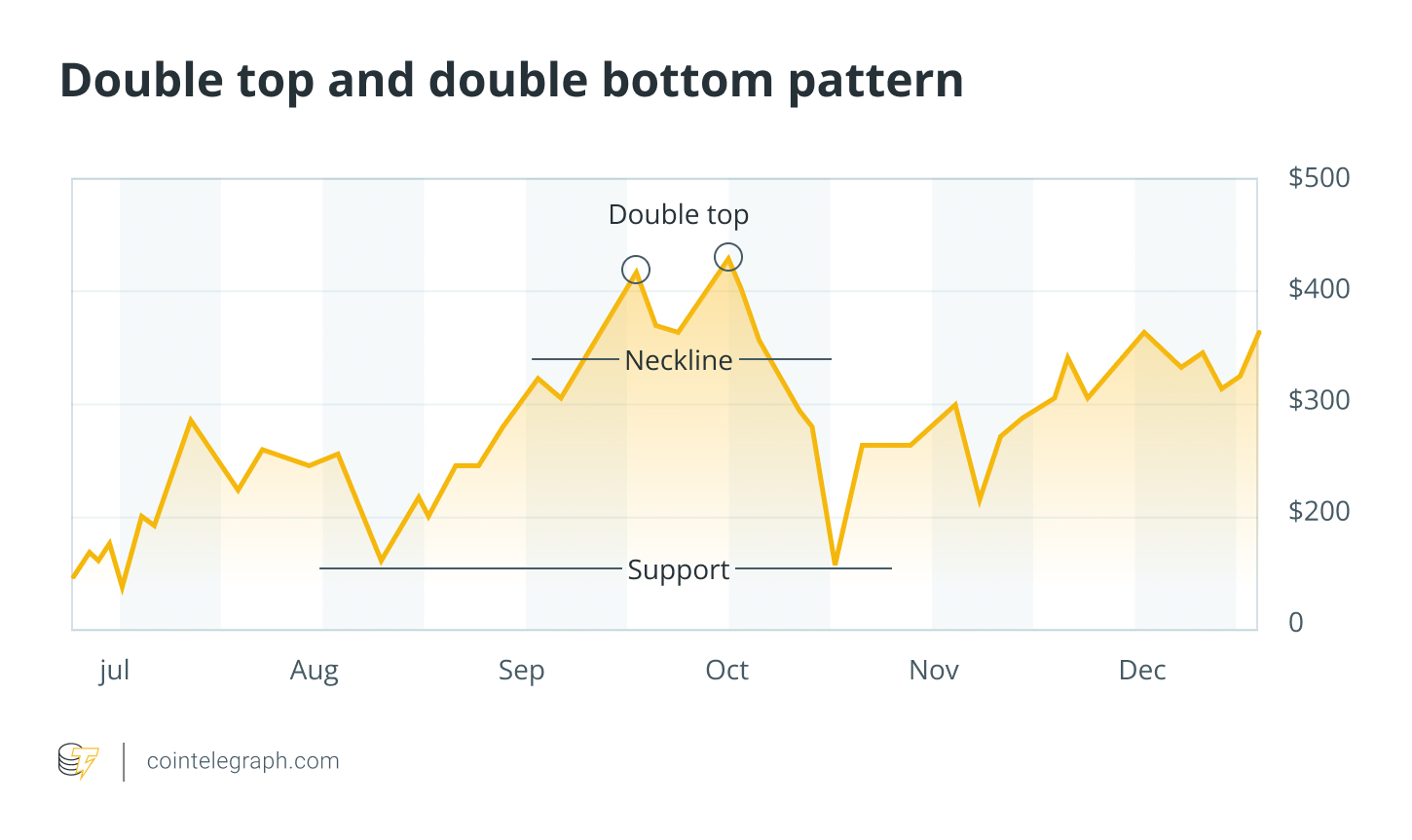
2. Double top and double bottom
The double tops form an “M” shape near resistance, indicating a potential bearish reversal. The double bottoms form a “W” shape near support, indicating a potential bullish reversal.
-
How to read: These patterns show two failed attempts to break resistance (top) or support (bottom). Confirmation occurs when the price crosses the neckline: bearish for double tops and bullish for double bottoms. Measure the rise from the neckline to the peaks or troughs, then project it from the breakout point to estimate movement.
-
Stop loss: Place it above the upper highs or below the lower lows.
-
example: This pattern often appears in memecoin pumps and dumps. For example, Dogecoin (Doug) formed a double top in mid-2025 after a social media-driven boom, followed by a sharp correction.
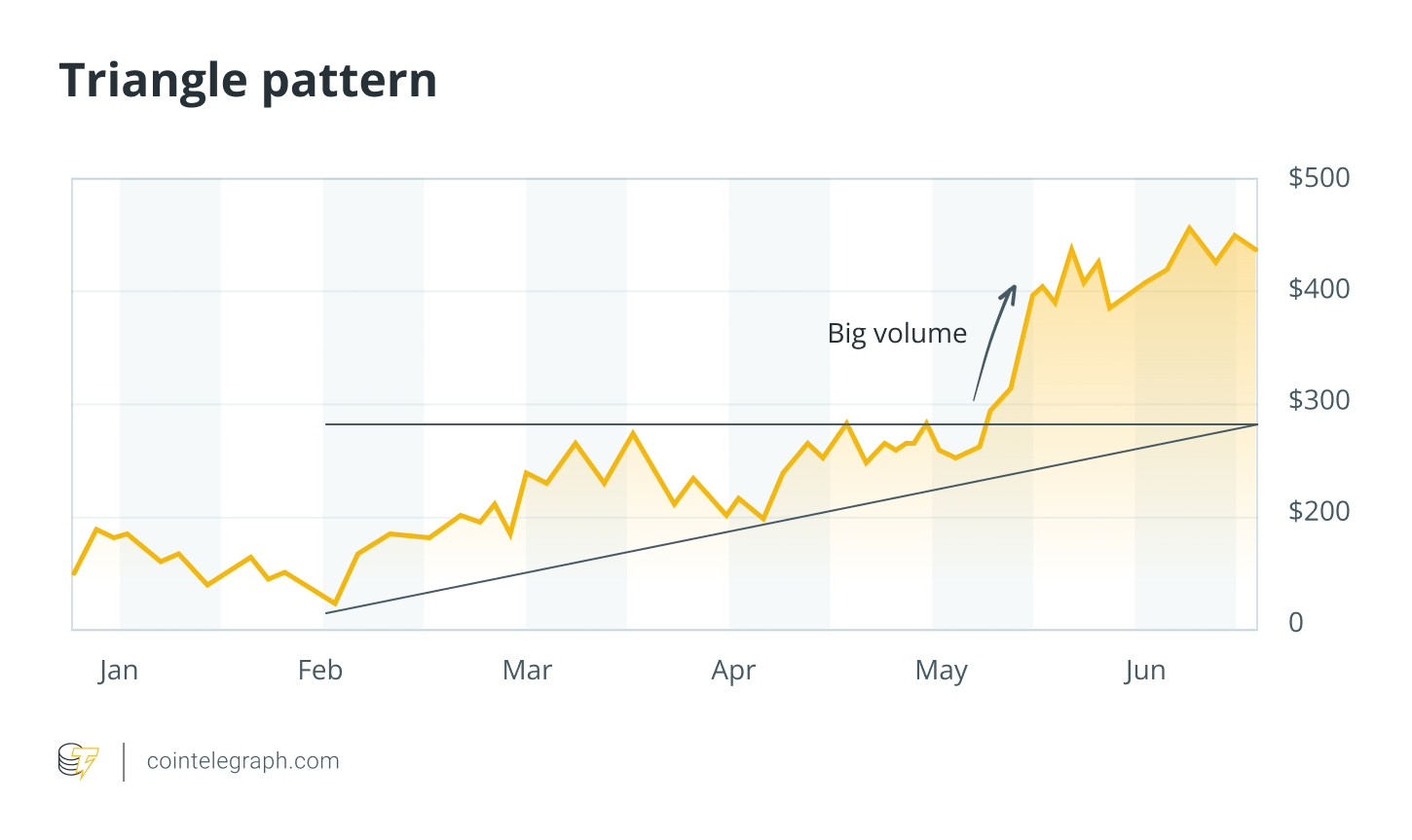
3. The triangle
Triangle patterns are formed when price movements create converging trend lines, resulting in a triangle shape. The three main types are bullish (bullish), bearish (bearish), and symmetrical (neutral).
-
How to read: Breakouts often follow the current trend but can sometimes reverse it. Estimate the target price by measuring the basic width of the triangle and projecting it from the breakout point. A breakout in an uptrend is usually bullish, while a breakout in a downtrend is bearish. To avoid false signals, use a 1%-2% filter before confirming the movement.
-
Stop loss: Place it below the triangle for bullish settings or above it for bearish settings.
-
example: During periods of market uncertainty, asset charts often display triangle formations. In early 2025, Ether (Ethereum) The price action formed a symmetrical triangle amidst the surrounding uncertainty Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Systems. The price later broke higher as regulatory clarity improved.
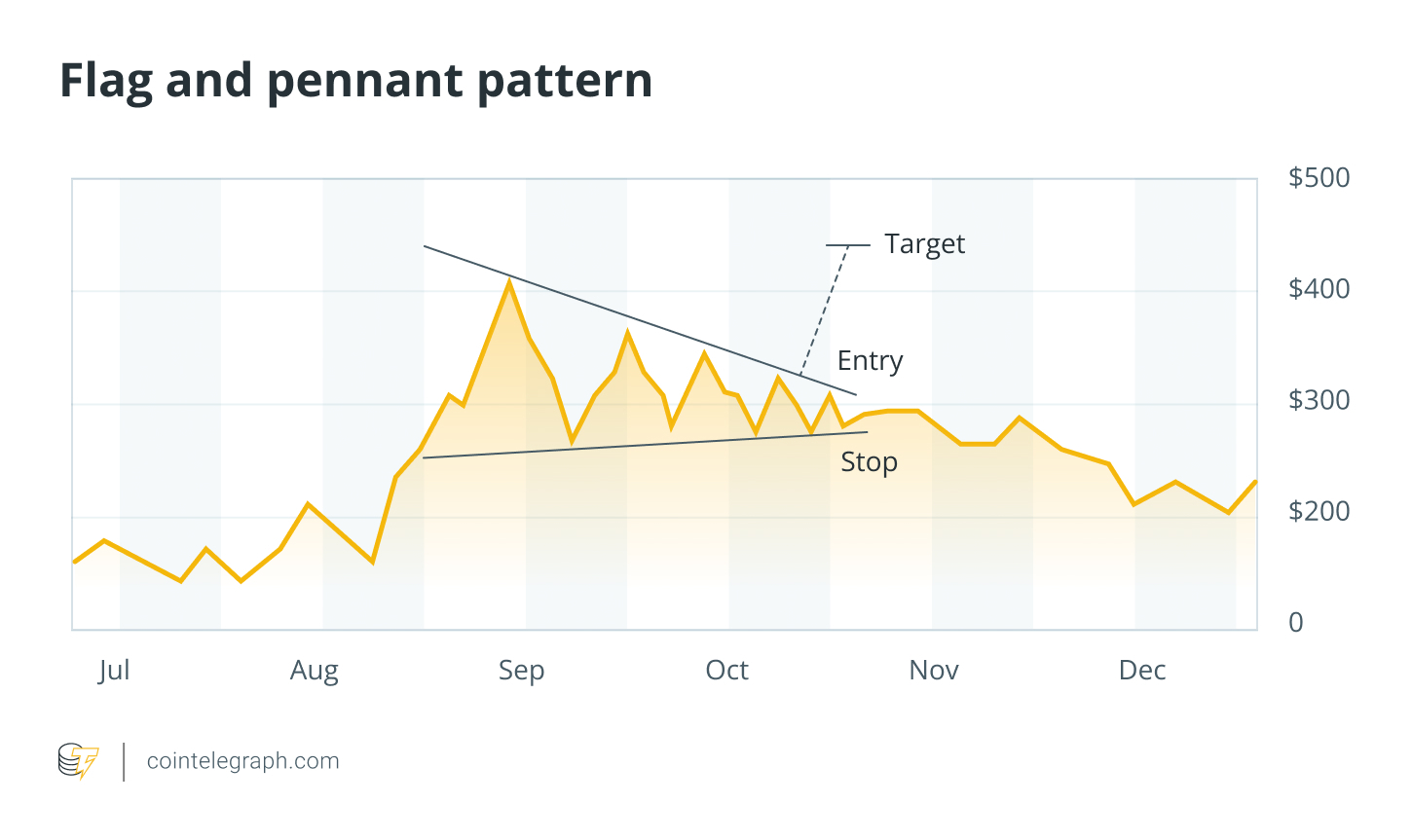
4. Flag and banner
Flag and pennant patterns are formed after sharp price movements. Flags appear as small parallel channels, while banners appear as compact triangles. Both signals pause before the prevailing trend continues.
-
How to read: A sharp “pole” followed by a short consolidation indicates that the trend is likely to resume. These patterns are bullish in uptrends and bearish in downtrends. On a pullback, traders often enter a flag or pennant to optimize their risk reward.
-
Stop loss: Place it below the low of the flag for bullish setups, or above the high for bearish setups.
-
example: During bull market phases, tokens often display flag or pennant formations. In 2025, Solana (Sol) The price action has formed a bull flag pattern amid the rapid growth of the ecosystem, including the launch of the new DeFi protocol. This setting indicates a continuation of the uptrend.
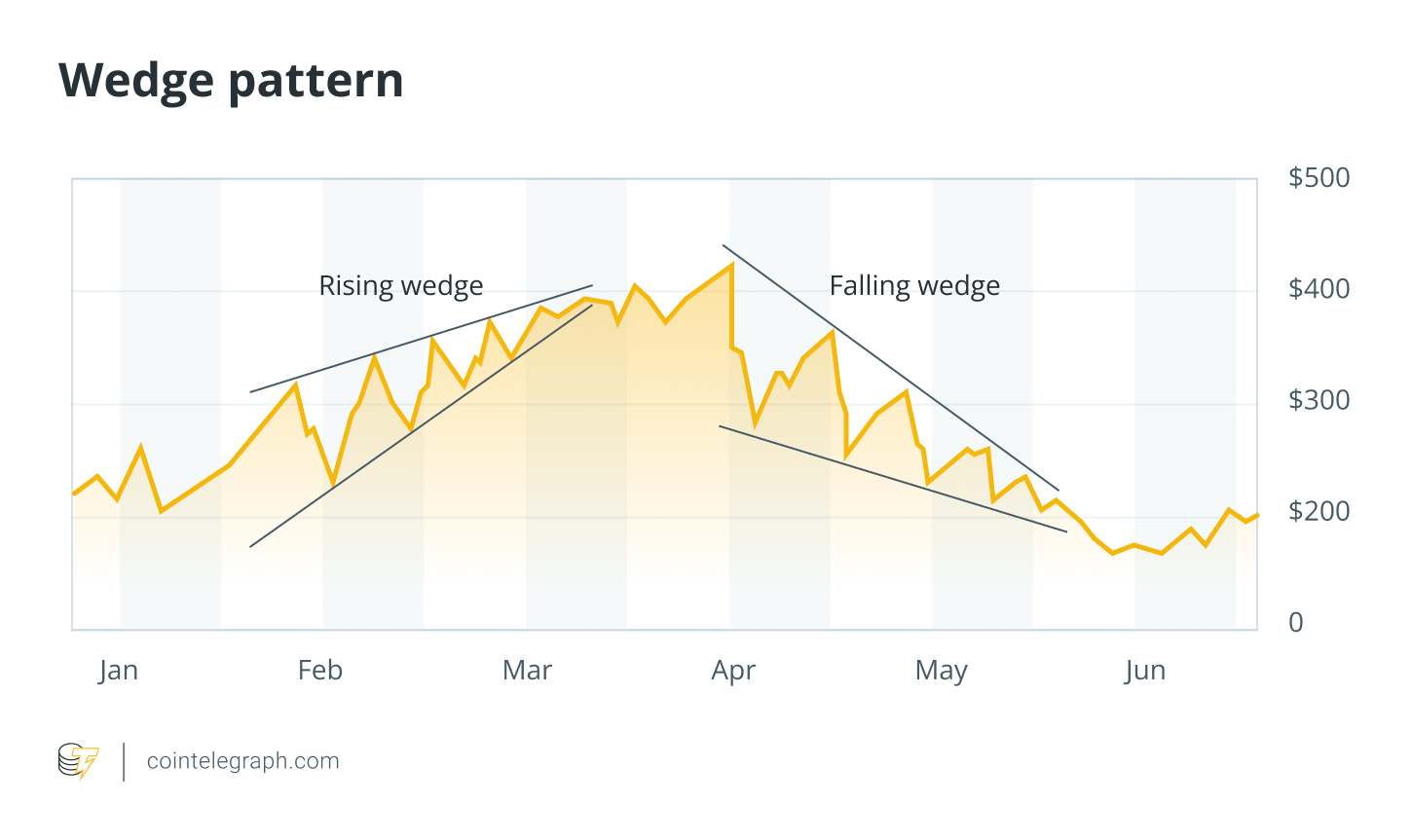
5. Wedge
Wedge patterns are formed when price action creates converging trend lines that slope either up (a rising wedge, usually bearish) or down (a falling wedge, usually bullish).
-
How to read: A rising wedge in an uptrend often signals a potential reversal with weakening momentum, while a falling wedge in a downtrend signals a potential bullish reversal. These patterns can also act as continuation signals when in line with the prevailing trend. Measure the height and width of the wedge from the breakout point to estimate the target movement.
-
Stop loss: Place it outside the opposite trend line of the wedge.
-
example: Wedge patterns can help identify potential market tops during overheated conditions. In 2025, during a period of heightened speculation, Arbitrum (ARB) The price action formed a rising wedge pattern, which was later followed by a market correction.
Did you know? Many cryptocurrency traders prefer logarithmic charts over line charts. While linear scales show absolute price changes, logarithmic scales highlight percentage changes, making it easier to compare Bitcoin’s early rise from $1 to $10 with its later move from $10,000 to $20,000, both of which represent 10x growth.
Supplementary tools and indicators for trend analysis
To enhance your trend analysis, you can use several Key indicators and tools. Important indicators include:
-
Moving Averages (SMA/EMA Crossovers): Track trends By monitoring when the short-term Exponential Moving Average (EMA) crosses above or below the long-term Simple Moving Average (SMA). The EMA gives more weight to recent price data, allowing it to respond faster to market changes, while the SMA calculates the average closing price over a specific period to get a smoother view of the overall trend.
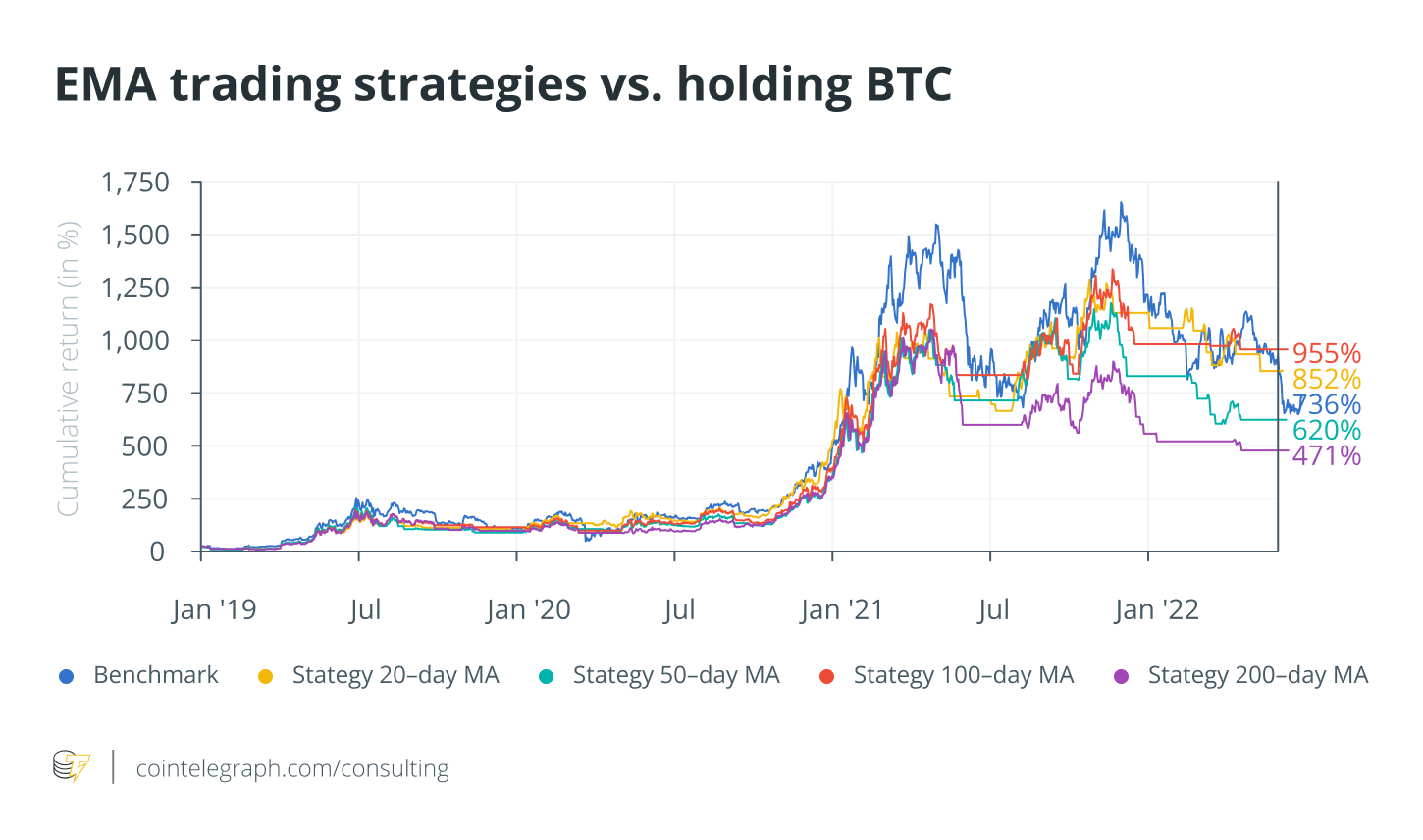
-
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detects overbought (>70) or oversold (prevents traders from chasing highs or exiting too early during corrections.
-
Moving Average Convergence/Divergence (MACD): The chart is used to identify momentum shifts when… The MACD line crosses the signal line. A widening gap between the two often indicates strengthening momentum.
-
Bollinger Band: Track fluctuations click on Detect potential breakthroughs or setbacks. When the price breaks above or below the bands, this indicates an upcoming move. Narrow bands indicate consolidation, which is often followed by sharp price fluctuations.
-
Size analysis: Volume spikes confirm market participation during breakouts or reversals, confirming the validity of chart patterns. Low volume during a trend can indicate weak momentum.
Did you know? Sound bars are more than just background images. They confirm whether price breakouts are trustworthy. High volume during a breakout indicates strong market participation, while low volume may warn of a false move. Many traders view volume as the “heartbeat” of chart analysis.
Risk management and best practices
Successful cryptocurrency trading depends on strong risk management and disciplined methods. Avoid analyzing patterns separately: instead, combine chart patterns with indicators (such as the RSI) and related news to improve accuracy. Always risk only a small portion of your capital to protect against sudden market fluctuations.
From a psychological perspective, resisting fear of missing out (FOMO) is essential in an AI-driven environment in 2025, where automated trading and social media can easily inflate asset prices. Stay grounded, avoid the hype and stay committed to your strategy.
Common mistakes include falling for false breakouts without confirming volume and over-trading on short time frames, which can lead to mental exhaustion. To enhance your approach, consider backtesting: applying your trading strategy to historical data to evaluate its past performance and potential future profitability.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risks, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.



