For anyone who still thinks of security as simple guards, fences and alarms, 2025 is a good year to refresh your mental image. Security now blends cameras, codes, algorithms, and sensors in ways that seem almost like science fiction
From small businesses to large corporations, security means monitoring doors and networks at the same time. Artificial intelligence, biometrics, blockchain, the Internet of Things, and even quantum computing are joining forces to keep people, data, and spaces safe.
Artificial Intelligence, the new brain of security
Artificial intelligence has become the brain Behind many security systems. It can look through hours of video or millions of data points much faster than any human and find patterns that seem “strange” or risky.
In physical security, AI helps smart cameras detect unusual movements or behaviors and quickly send alerts. In digital security, it reviews network traffic, searches for strange connections, and blocks threats in near real-time
The main advantage is that Artificial intelligence learns from past events. With each attack or suspicious event, the models improve, making future detection more accurate and reducing the number of false alarms
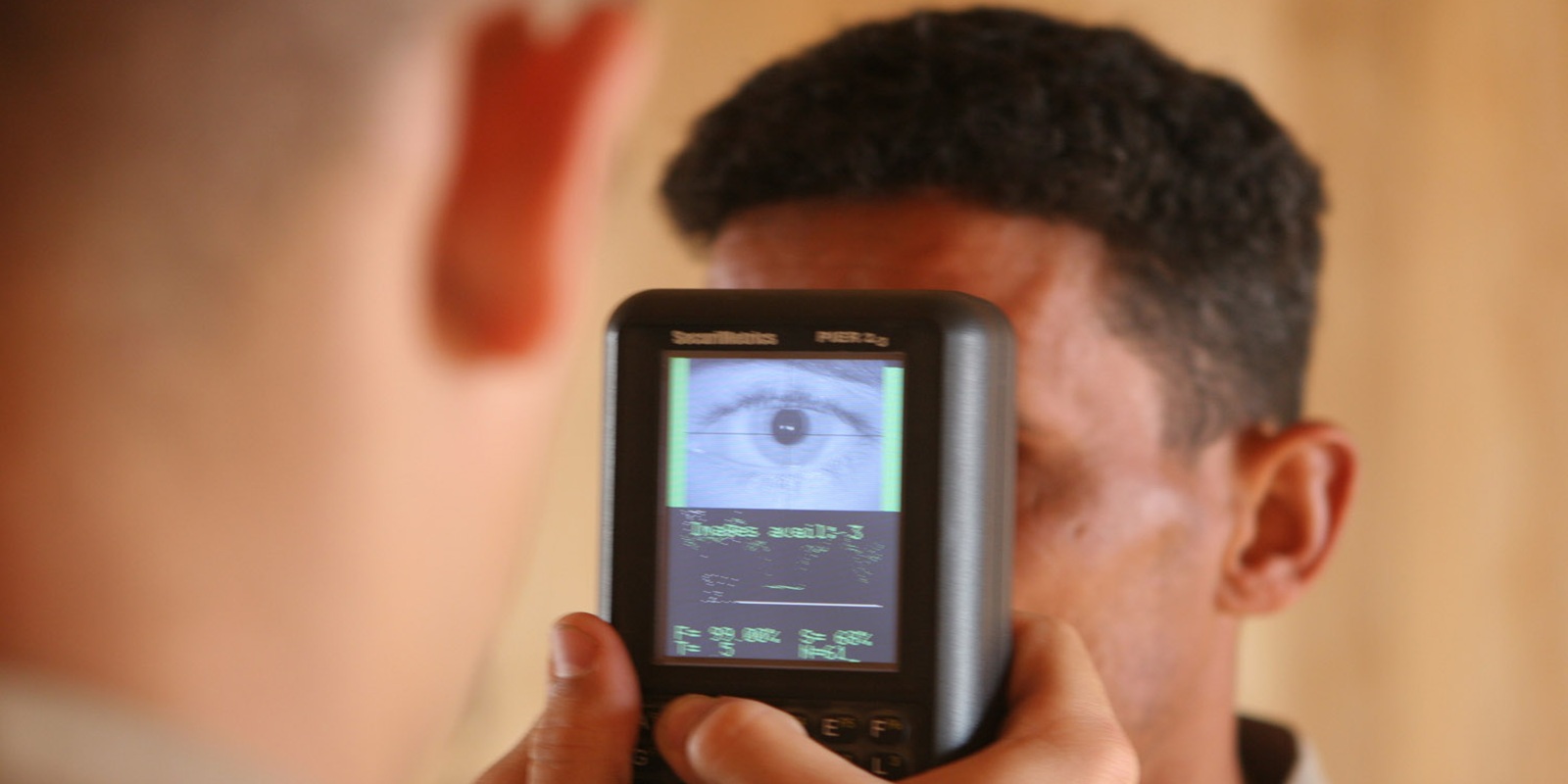
Biometrics, from fingerprints to seamless access
Biometric security, which uses unique Characteristics such as fingerprints or faces have quietly moved from spy movies into everyday life. Many phones are already unlocked using a fingerprint or facial scan instead of a PIN
In businesses, biometrics replaces legacy access cards that can be lost or shared. Employees can enter offices using facial recognition, voice scanning, or retina scanning, which links access directly to the person, not a plastic badge.
Online services are also adding biometrics to their login process. Instead of just typing a password, users confirm their identity with their fingers or faces, providing simple but much stronger protection for banking and other sensitive accounts.
Blockchain and data that cannot be “edited”
Blockchain, or block chain, is a technology that stores information in linked records that are difficult to change. Once data is written, it becomes very difficult to change it without leaving a visible trace
This feature is useful for security because it helps ensure that records, contracts, or transaction histories are not secretly modified. It adds a layer of trust in digital environments where cheating is difficult to see
In cybersecurity, blockchain technology can support secure identity systems, protect records from tampering, and power “smart contracts” that only trigger automatically when all conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Internet of Things, everything is connected, and everything is vulnerable
the The Internet of Things connects everyday devices To the Internet. Cameras, alarms, motion sensors, thermostats, and even lights now talk to each other and to central platforms that monitor entire buildings or even entire neighborhoods.
This connectivity helps security teams see everything from one dashboard. For example, a single application can display camera feeds, door status, alarm events, and even trigger responses based on predefined rules.
However, each connected gadget is also a small door that hackers may try to open. If a device has weak passwords or outdated software, it can become an easy entry point into larger systems
For this reason, IoT security needs strong defaults, regular updates, and careful network design. Otherwise, a smart camera intended for building protection could turn into a danger instead.
Quantum security, the next big leap
Quantum computing It uses the rules of quantum physics to process information in new ways. While it’s still early days, it’s expected to solve some problems, including some types of encryption, much faster than regular computers.
This creates both promise and challenge. On the one hand, quantum technology could enable nearly unbreakable encryption of highly sensitive data. On the other hand, it can eventually break many popular algorithms today
For this reason, researchers are already working on “post-quantum” cryptography. The idea is to design new methods that remain secure even when quantum computers become powerful enough to threaten legacy systems
Modern security is no longer a single-layer shield. It is a combination of artificial intelligence, biometrics, blockchain technology, the Internet of Things and quantum ideas that work together to protect the physical and digital worlds. As these technologies grow, businesses and users will need to stay informed and proactive. Tools are more powerful than ever, and so are threats, so smart use and constant updates will be part of everyday security life.