a summary: Take a second look at the data associated with bitcoin. We note that, according to the number of transactions, the distinctive BRC-20 symbols are the dominant form of orders, with 92.5 million BRC-20 transactions compared to 2.7 million Tartin images of ONSAIN. However, when it comes to the amount of data, the ceremonies related to pictures are almost the same as the BRC-20 orders, at about 30 GB. We explain that from the point of view of the node hostility, the smaller BRC-20 relevant transactions, which have a reasonable structure similar to “regular transactions” are great negative. In contrast, the ceremonies related to pictures are larger in size and contain more “arbitrary data”, and this has a positive effect on node resources. Therefore, BRC-20 codes may be a concern for some contestants in the knot.
summary
In February 2023, when it was the alleged boom, it was just a running, we analysis Blockchain to produce our first report on this topic. In this piece, we take a second look at the associated data associated with the Bitcoin Blockchain and in particular we evaluate the impact of this data on the resources needed to operate the full Bitcoin node.
Overview of the datab data by type
Since the crazy madness began, there have been about 97.4 million inscriptions on Blockchain Bitcoin. Among them, the overwhelming majority, according to the Count, were linked to the BRC-20 symbols, either symbolic mint or symbolic transfers. On the contrary, there were about 2.7 million engraved pictures in Bitcoin Blockchain, as the table shows below.
| He writes | number |
|
BRC-20 |
92,514,620 |
|
image |
2,710,087 |
|
last |
2,048,399 |
|
video |
100,321 |
|
Vocal |
1525 |
|
634 |
|
| the total | 97,375,586 |
source: https://dune.com/dgtl_assets
Total inscriptions so far – by counting
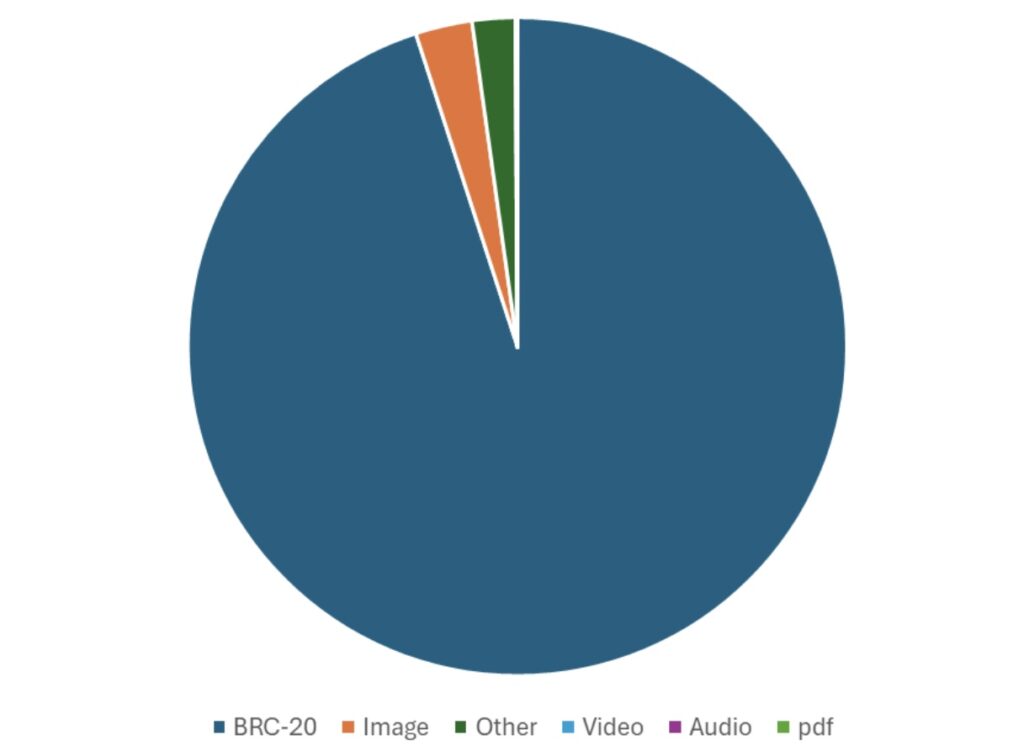
source: https://dune.com/dgtl_assets
Although the BRC-20 is dominant in relation to the number of related transactions, when it comes to the data used, the story is more mixed. In raw bitules, arrangement and other data take about 30.0 GB of Blockchain space. This is slightly more than 27.8 GB of data taken by BRC-20 relevant transactions. Therefore, when it comes to initial data, the effect of images is almost like the distinctive BRC-20. Regarding the superior weight, the images benefit from the deduction of witnesses, so that they benefit from 8.9 billion units of weight, which is much lower than the distinctive BRC-20, which used 13.9 billion units of weight so far.
| Data size (MB) | Virtual Baits (M) | Fees (BTC) | Average Feera (SAT/VB) | |
|
BRC-20 codes |
27,813 |
13,912 |
5,072 |
36.5 |
|
Pictures and the other |
29,957 |
8,935 |
2,012 |
22.5 |
|
Non -arrangement transactions |
183,942 |
119,016 |
33,236 |
27.9 |
| the total | 241,712 | 141,863 | 40321 | 28.4 |
Source: bitmex research. Notes: Data from December 2022 to September 2025
The costs of operating the node – theory
In terms of the costs of operating the knot, in theory, large arrangement images should be easier to verify the regular transactions for each unit of the mass weight. This is because the images are engraved in a non -executive part of the Taproot witness. Therefore, there are no signatures to verify, which may be the most important part of running the knot. The arrangements are also useful for expanding their scope in other ways, as the hungry data of the data takes a Blockspace distance that can be used to increase the UTXO collection. Therefore, in general, data related to abuse of abuse can be positive, when it is purely viewed from the point of view of the validity of Blockchain.
On the other hand, BRC-20 relevant transactions have more similar properties with normal transactions related to bitcoin. BRC-20 transactions are smaller in size and have less arbitrary related data, and therefore from the perspective of the node’s hostility, they should be in the same regular transactions regarding the knot resources required to verify health. However, the main problem with BRC-20 codes, from the scaling perspective, is that it blows the UTXO group. As a result, to a large extent of the distinctive BRC-20, the UTXO group increased from 84 million to 169 million, in the Territory period from December 2022 to September 2025. This is an increase of about 85 million outlets. The size of the UTXO group is a major measure of hostility in the knot, especially the saturated nodes, and therefore the presence of the distinctive BRC-20 materially harmful to these operating nodes. However, transactions outputs do not benefit from the deduction of witnesses, and therefore the BRC-20 related transactions paid a higher rate per vicinity of this block space. BRC-20 transactions pushed more than 5000 Bitcoin in transactions fees, where the BRC-20 protocol was invented.
UTXO set size
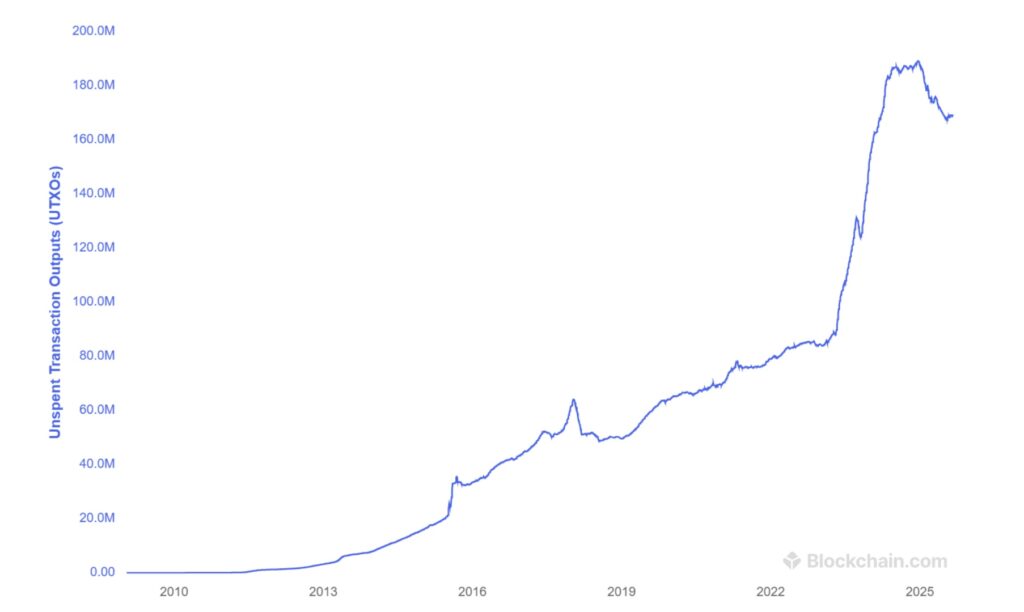
source: https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/charts/utxo-count
Results of the accommodation of the node
We conducted several tests, and the first Blockchain download. We used a UBUNTU computer, with 8 CPU and 8 GB of RAM. The machine had a 1 TB capacity and 1 GB internet connection. One of the potential criticisms of our analysis is that this speed speed was very fast and that the contract at home may have a slower network, which may make it take longer to download large orders. The test was done with version 29.1 Bitcoin Core. The aim of the performance test was to assess the extent of the node download, check the blocks, and the decline in these speeds in exchange for the amount of data associated with each block. In the charts below, each point is one day. The coordinates of the Xi Axis represent the number of blocs that were verified per second every day. The axis of the axis of Y is the average amount of data related to each block every day or the average size of each arrangement per day.
The results with a valid assumption = 1 (skipping verification signature)
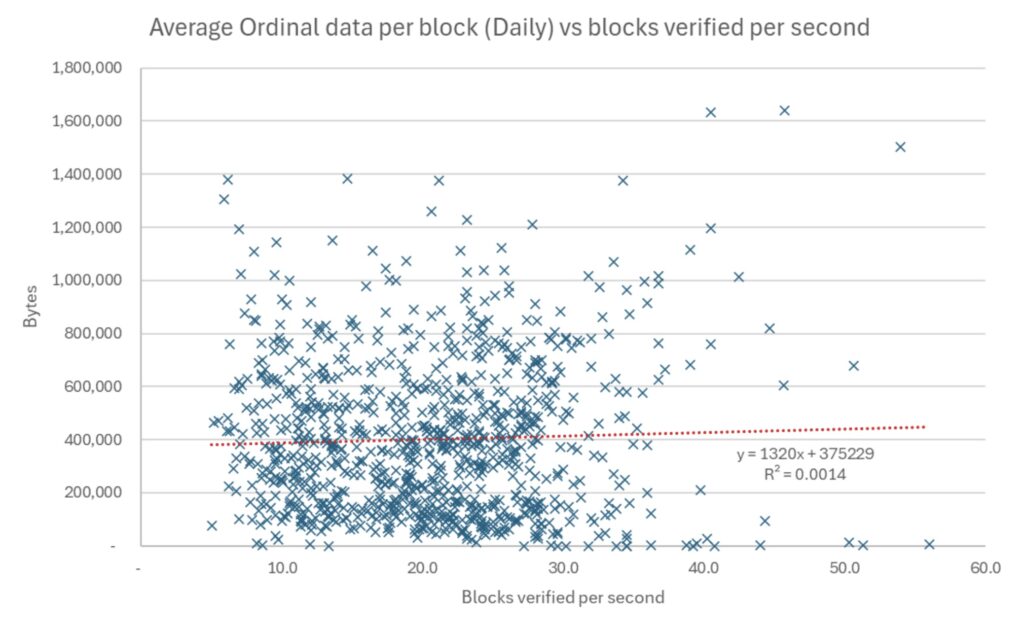
Source: bitmex research. Notes: Data from December 2022 to September 2025, 959 days
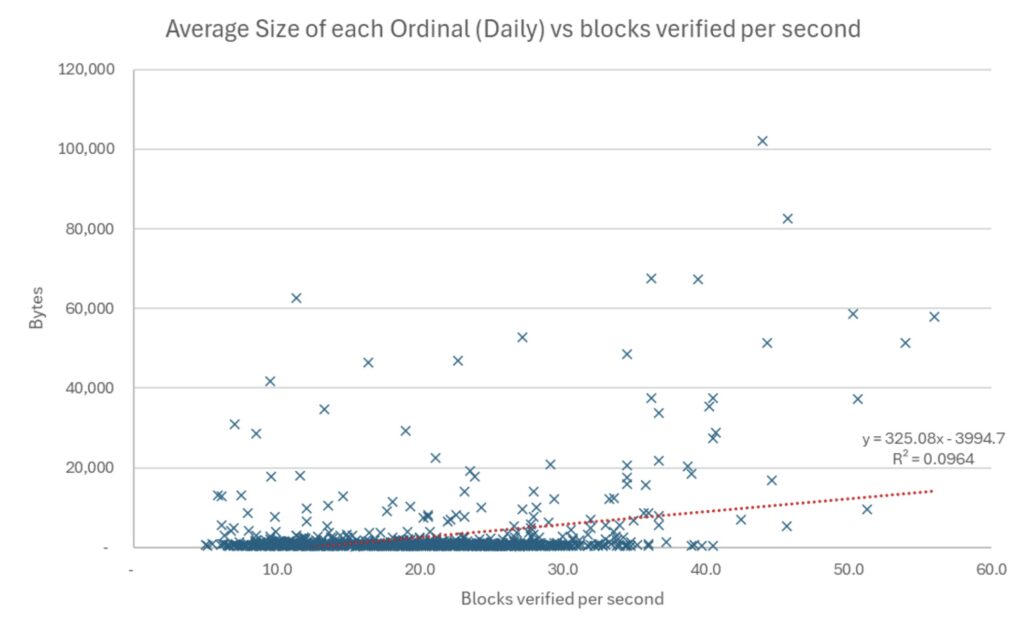
Source: bitmex research. Notes: Data from December 2022 to September 2025, 959 days
Results with a valid assumption = 0 (Carry out all signing verification operations)
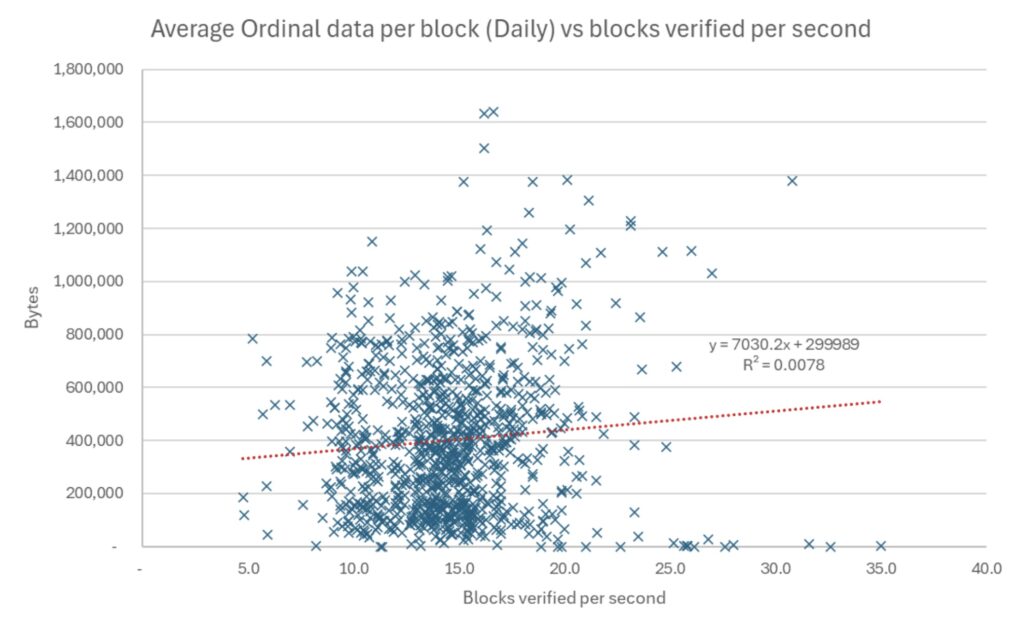
Source: bitmex research. Notes: Data from December 2022 to September 2025, 959 days
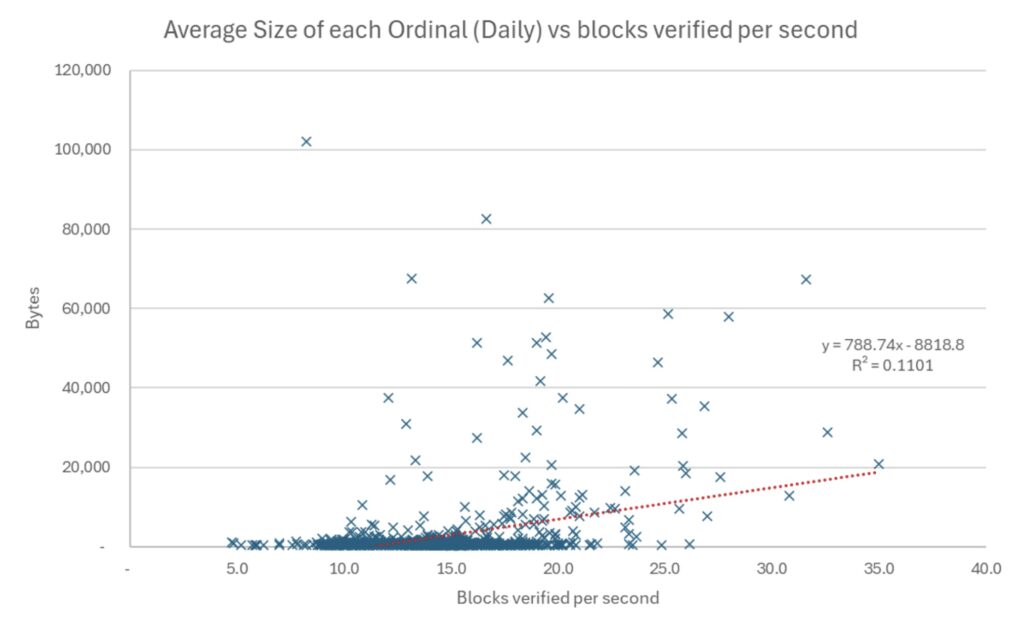
Source: bitmex research. Notes: Data from December 2022 to September 2025, 959 days
The results are reasonably inconclusive, however, each slope showed a positive relationship between the amount of arrangement data and the speed of verification. There will always be a lot of randomness when it comes to downloading data on an online counterpart online, so it may be understood that the results are reasonably weak. Random problems in the disk can also cause differences in speed. Therefore, one should be somewhat skeptical of these results and we publish this in the hope that others will repeat or improve this experience.
A major part of theoretical logic, why should the Tartin data be accelerated in verifying that the assumption that the blocks are always full. If the arbitrary data decomposes transactions data, this verification must accelerate. However, the blocs are often full but not always 100 % full. Unusual blocs mean that more arbitrary data slows down the block. Therefore, in this period, December 2022 to September 2025, these two factors may play against each other. This effect may be noticeable when Sarter is turned on, as the arrangement data for each block has a square relationship with only 0.1 % verification. Therefore, there is no evidence of a relationship here.
There is some logic for the results, with the assumption that it has been turned off, the positive relationship between the arrangement and the speed of verification increases. Suppose its righteous turning off is the best way to test it, because once your knot is synchronized to the edge, it checks the signatures and this is the case for most of the contract. The most powerful R value of the test is 11 %, when it is supposed to be turned off, and when we compare the speed of checking with an average arrangement volume. Daily data may indicate that the mass verification becomes faster with an increase in the average arrangement and that 11 % of the contrast can be explained at the time of verification by larger stages.
conclusion
The above analysis does not mean that the large related images are a good or positive thing for bitcoin. These images can have long -term negative effects on the system, as financial transactions may be priced, which can have all kinds of negative consequences. All the data in this report is that large arrangement images may have a small side benefit, partially compensates for potential negatives, which is that more arbitrary data on the chain, if performed well, may make it easier to run a knot in practice.





