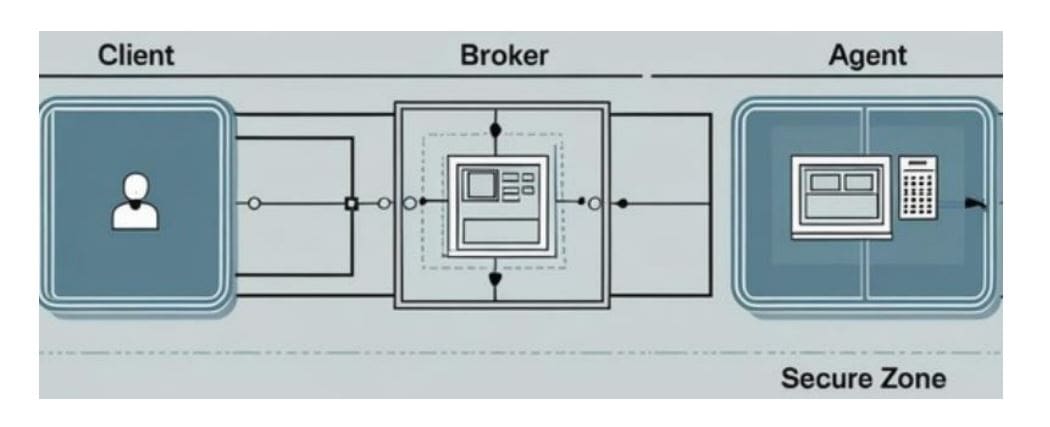
The increasing reliance on artificial intelligence requires new methods of dealing with security, especially as threats become more complex. I. presents. Al-Sharqawi, and C. Clark, and J. Horgan, and I. Dai is an innovative framework that combines post-quantum cryptography and zero trust architecture, formally built on the foundations of category theory, to protect access to artificial intelligence models. This innovative work models cryptographic operations as mathematical transformations and trust policies as functions, allowing fine-grained and adaptable trust management and detailed security hashing for advanced cryptosystems. By demonstrating a practical implementation on ESP32 hardware, the team validates the flexible transition to quantum-resistant security, achieving significant memory efficiency and successfully blocking all unauthorized access attempts with remarkably fast performance, thus creating a new standard for AI security.
Category theory secures artificial intelligence through post-quantum cryptography
This study drives a new security framework that integrates post-quantum cryptography (PQC) and Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) using the formal language of Category theoryThis enables strong protection of AI models against advanced threats. Researchers model cryptographic workflows as mathematical “forms,” and trust policies as “actors” within this framework, allowing fine-grained, adaptive trust and fine-grained hashing for network-based PQC primitives. This approach systematically captures the interactions between cryptographic elements and access control elements, providing an algebraically consistent description of secure systems and enhancing protection against adversarial AI. To demonstrate a practical implementation, scientists designed a concrete system based on the ESP32 microcontroller, validating the move to fast cryptographic security with quantifiable performance gains.
The implementation achieves exceptional memory efficiency, with the proxy using 91.86% and the broker 97.88% of the available free heap after encryption operations, demonstrating suitability for resource-constrained devices. Rigorous testing has confirmed that the system successfully rejects 100% of unauthorized access attempts with an average access time of less than a millisecond, highlighting its effectiveness in real-time security applications. The researchers used Engel expansions to generate deterministic randomness from the seed, providing a structure for security proofs while simultaneously reducing the communication and storage costs associated with generating a large matrix.
This technique enhances the non-decreasing and chaotic properties of Engel coefficients under mixing, leading to a nonlinear iteration that avoids potential linear dependencies that can be exploited in reduction attacks. Furthermore, the study used category theory to represent probabilistic effects using “monadism,” distinguishing between deterministic logic and inherent randomness within the system. This abstraction allows encryption of parameterized schemas and facilitates formal proofs of security, going beyond traditional approaches that treat objects as unstructured collections.
AI security via category theory and PQC
This work presents a new security framework for AI models, integrating post-quantum cryptography (PQC) and zero-trust architecture (ZTA) using principles from category theory. The key breakthrough lies in modeling cryptographic workflows as mathematical “forms” and trust policies as “actors,” enabling fine-grained adaptive security for network-based PQC primitives. This approach clearly enhances protection against adversarial threats targeting AI systems. The main outcome of this research is a practical implementation on the ESP32 platform, validating the transition to fast cryptographic security with measurable improvements.
The implementation achieves exceptional memory efficiency, with the proxy using 91.86% and the broker 97.88% of the available free heap after encryption operations. Most importantly, the system successfully rejected 100% of unauthorized access attempts with an average access time of less than a millisecond, demonstrating strong real-time performance. Experiments involving 1000 message encryptions show a high degree of consistency, empirically confirming the validity of theoretical predictions.
the Wasserstein distance,Measuring differences in ciphertext distributions,remained minimal, confirming perfect message recovery. The team demonstrated a reduction in the computational complexity of LWE applications by reducing key sampling and matrix multiplication operations, resulting in a significant reduction in the overall computational cost. This research proves that the categorical framework preserves both computational security and functional correctness during parameter changes.
Access to AI is secured by post-quantum trust
Researchers have successfully demonstrated a formally verified, practical security system that integrates zero trust architecture and post-quantum cryptography, designed to protect access to artificial intelligence models. Supported by the mathematical framework of category theory, this system demonstrates survivability even on resource-limited devices, such as the ESP32 microcontroller. Experimental results confirm the practical benefit of mesh encryption in low-end systems, with average encryption and decryption times of 10.97 ms and 2.89 ms, respectively, minimizing the impact on overall latency.
The system achieved a 100% rejection rate for unauthorized access attempts with an average access time of less than a millisecond, while maintaining minimal resource consumption while mitigating the attack. It is worth noting that the categorical framework enables cryptographic flexibility, which significantly reduces the code modifications required when switching between cryptographic algorithms. This work presents a robust, quantum-resistant, and adaptable solution to real-time, resource-constrained environments, which is critical for further deployment of AI in IoT and edge computing applications.